LESSON H5P - Loads and Forces
The absolute basics. And a practical lesson about our bodies.
The back.
The back is considerably more complicated than the arm or leg, with various muscles and joints between vertebrae, all having mechanical advantages less than 1. Back muscles must, therefore, exert very large forces, which are borne by the spinal column. Discs crushed by mere exertion are very common. The jaw is somewhat exceptional—the masseter muscles that close the jaw have a mechanical advantage greater than 1 for the back teeth, allowing us to exert very large forces with them. A cause of stress headaches is persistent clenching of teeth where the sustained large force translates into fatigue in muscles around the skull.
Figure 2 shows how bad posture causes back strain. In part (a), we see a person with good posture. Note that her upper body’s cg is directly above the pivot point in the hips, which in turn is directly above the base of support at her feet. Because of this, her upper body’s weight exerts no torque about the hips. The only force needed is a vertical force at the hips equal to the weight supported. No muscle action is required, since the bones are rigid and transmit this force from the floor. This is a position of unstable equilibrium, but only small forces are needed to bring the upper body back to vertical if it is slightly displaced. Bad posture is shown in part (b); we see that the upper body’s cg is in front of the pivot in the hips. This creates a clockwise torque around the hips that is counteracted by muscles in the lower back. These muscles must exert large forces, since they have typically small mechanical advantages. (In other words, the perpendicular lever arm for the muscles is much smaller than for the cg.) Poor posture can also cause muscle strain for people sitting at their desks using computers. Special chairs are available that allow the body’s CG to be more easily situated above the seat, to reduce back pain. Prolonged muscle action produces muscle strain. Note that the cg of the entire body is still directly above the base of support in part (b) of Figure 2. This is compulsory; otherwise the person would not be in equilibrium. We lean forward for the same reason when carrying a load on our backs, to the side when carrying a load in one arm, and backward when carrying a load in front of us, as seen in Figure 3.

Figure 2. (a) good posture places the upper body’s cg over the pivots in the hips, eliminating the need for muscle action to balance the body. (b) Poor posture requires exertion by the back muscles to counteract the clockwise torque produced around the pivot by the upper body’s weight. The back muscles have a small effective perpendicular lever arm, rb⊥, and must therefore exert a large force Fb. Note that the legs lean backward to keep the cg of the entire body above the base of support in the feet.
You have probably been warned against lifting objects with your back. This action, even more than bad posture, can cause muscle strain and damage discs and vertebrae, since abnormally large forces are created in the back muscles and spine.

Figure 3. People adjust their stance to maintain balance. (a) A father carrying his son piggyback leans forward to position their overall cg above the base of support at his feet. (b) A student carrying a shoulder bag leans to the side to keep the overall cg over his feet. (c) Another student carrying a load of books in her arms leans backward for the same reason.
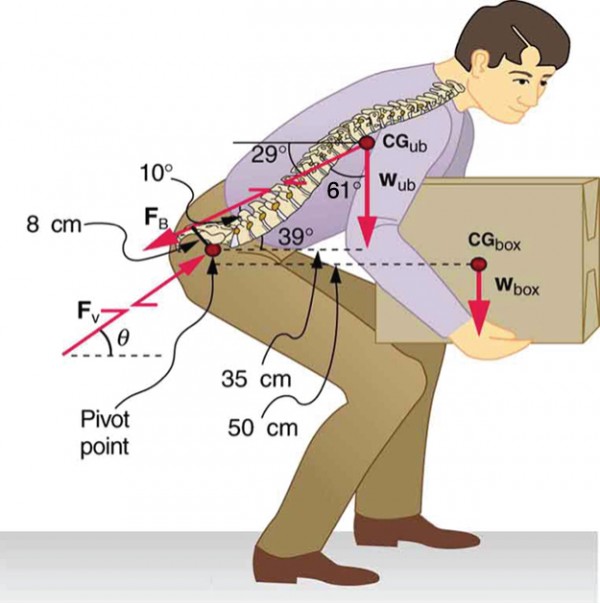
Figure 4. This figure shows that large forces are exerted by the back muscles and experienced in the vertebrae when a person lifts with their back, since these muscles have small effective perpendicular lever arms. The data shown here are analyzed in the preceding example, Example 2.
What are the benefits of having most skeletal muscles attached so close to joints? One advantage is speed because small muscle contractions can produce large movements of limbs in a short period of time. Other advantages are flexibility and agility, made possible by the large numbers of joints and the ranges over which they function. For example, it is difficult to imagine a system with biceps muscles attached at the wrist that would be capable of the broad range of movement we vertebrates possess.
There are some interesting complexities in real systems of muscles,
bones, and joints. For instance, the pivot point in many joints changes
location as the joint is flexed, so that the perpendicular lever arms
and the mechanical advantage of the system change, too. Thus the force
the biceps muscle must exert to hold up a book varies as the forearm is
flexed. Similar mechanisms operate in the legs, which explain, for
example, why there is less leg strain when a bicycle seat is set at the
proper height. The methods employed in this section give a reasonable
description of real systems provided enough is known about the
dimensions of the system.
